Share
This Sustainable Life
538: How much should I reduce my pollution? How many slaves should Thomas Jefferson have freed?
Here are the notes I read from for this episode:
Will hit 70 next week.
Dawning on people what has dawned on what we now call the global south, that the projections are more serious than they internalized. That their world is going to be rocked. Maybe they realize, that this will be the coldest Christmas for the next ten thousand years and that billions of people may be displaced. Maybe they realize that you can't move billions of people without many of them dying. The global north, including you, will not let more people into the country than are there now..
Many people considering polluting less. A few asking me about not flying, which for years no one would consider.
But their life depends on polluting activities. They didn't ask for system. What can they do, never see their family again? Think of all the good they can bring the world.
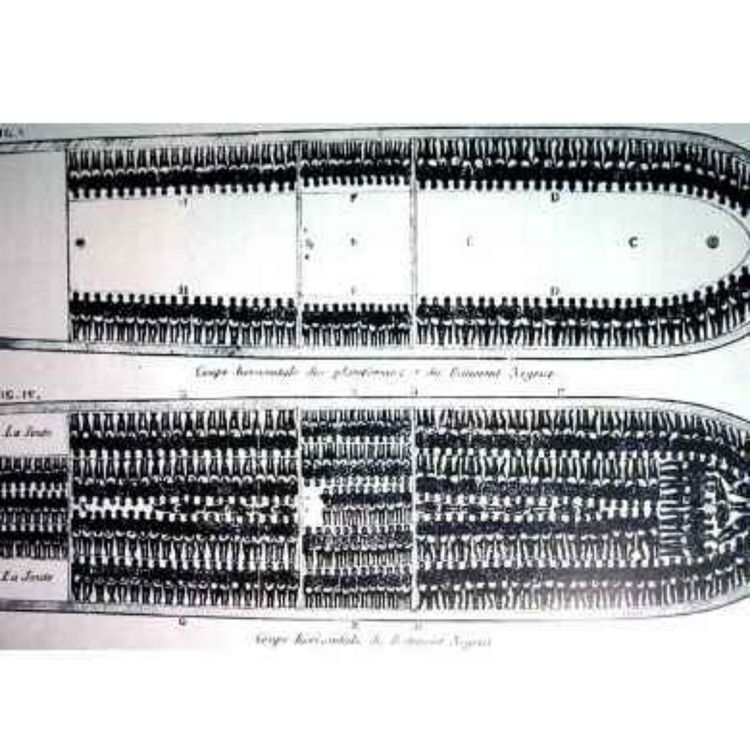
They just took down Thomas Jefferson's statue. Should they have? What excuse for owning slaves?
He inherited. Didn't ask for. Owning them allowed him to spend more time with family. Look at what it enabled him to do
Should he have sold them and made money? What if just freeing them bankrupted him? Left him with no way to contribute to world? It wouldn't have stopped slavery.
If your reason for traveling is work, instead of Jefferson, ask about some guy with an empty slave ship in Africa. He got investors and took out mortgages. It was a legal deal. He has investors to pay back. He may even have believed he was bringing backward people to civilization. So he's got an empty ship and he's an ocean from home. They didn't pack people into ships for their own health. Their business model required them to bring that many. If he brings a full load of slaves to the colonies, he can at least get home after dropping them off. Let's say for the sake of argument that if he doesn't trade them, he will make no change whatsoever to the system. How many slaves should he bring on this trip? How many more trips should he take? Is there any question he's hurting people?
How many more flights should you take? How much meat should you eat? How much plastic should you use? Do you wonder if your actions are causing people to suffer? Let's say for the sake of argument that your actions won't change the system whatsoever.
Why do we learn history if not to learn from it, not repeat its mistakes.
I had to struggle with these questions and challenges when I chose to avoid meat, packaged food, and flying. I don't know why you would think it's harder for you than for me, Thomas Jefferson, or the slave trader. It wasn't for me and if you stop and think for a bit you'll realize people will think it was easier for you and you'll realize how dehumanizing and insulting they will be of your struggle, so you may see how ignorant and insensitive you are being toward me.
But I do know you'll be glad when you realize what's right for you and the the people in the global south. That history will view you like the slave owner, no matter your skin color. Of course many differences between the system of slavery and the system of pollution, but the biggest one is that our system today produces much more suffering and death. 10M annually versus centuries. But it twists people into acting against their values, thinking more of themselves than the people they torture. What else could I do, not see my family?
The liberation and freedom you feel on the other side of the difficulty of realizing you yourself will enjoy life more and be able to get everything you wanted from it when you stop doing what you know kills others.
It's not fair. We didn't create this system. We didn't ask for it. If people before hadn't set it up, we'd never create it. We didn't ask to be born. We want to help the people being hurt. But all of that counterfactual doesn't change that we do live in this world as much as Thomas Jefferson did.
More episodes
View all episodes

847. 847: Tzeporah Berman: Ending Fossil Fuels by Treaty
47:42||Ep. 847I met Tzeporah at an event called Climate Week NYC last fall. She was nearly the only person there who spoke about decreasing and stopping extracting fossil fuels. I had to bring her here.Our conversation grew more compelling and interesting as we spoke. The early parts about energy sources besides fossil fuels you may have heard before, but give context.After she shares the realizations that prompted her to lead are what I valued. In particular, she exposes and clarifies how people have simply ignored fossil fuel production or extraction in favor of accounting methods and seeing if they can offset things but not decreasing extraction.She also talked about her strategy, which differs from Paris Agreement approaches and is based on how treaties on land mines and chemical weapons succeeded. She also shares some eye-popping statistics, like how much fossil fuels are used just to transport other fossil fuels, which is just over two-thirds.The bottom line is almost too simple to say, but it bears repeating: we have to stop extracting fossil fuels fast. Tzeporah is one of the few working on, undistracted by things that don't stop us from extracting them.The Fossil Fuel Treaty InitiativeHer TED talk: The bad math of the fossil fuel industryHer book: This Crazy Time: Living Our Environmental ChallengeHer Wikipedia page
846. 846: Gail Eisnitz: The Inside Story of a Life Investigating Factory Farms
01:00:13||Ep. 846Gail shares her investigations into meat industry practices, exploring how exorbitant slaughterhouse production line speeds in a consolidated slaughter industry affect animals as they are being handled and killed, and how the proliferation of massive factory farms impacts animals being raised in intensive confinement.She spent decades in the field documenting violations against farm animals and in the office preparing cases and writing about her investigations in articles and books. Her efforts to expose and prosecute animal abusers were often thwarted by network television producers and by law enforcement authorities. Producers considered her findings too disturbing. The law refused to prosecute abusers. Instead they provided cover for the meat industry---a billion-dollar industry.She gives an inside view behind the closed doors of U.S. slaughterhouses and factory farms. She also shared her challenges and successes in documenting and exposing the findings.As a memoir, Out of Sight has been described by reviewers as a “detective story” and a “page turner” that they “can’t put down," probably for her personal challenges related to her diagnosis with a rare medical visual condition she shares in our conversation.Gail's web pageThe Humane Farming AssociationHer most recent book: Out of Sight An Undercover Investigator's Fight for Animal Rights and Her Own SurvivalHer first book: Slaughterhouse The Shocking Story of Greed, Neglect, and Inhumane Treatment Inside the U.S. Meat Industry
845. 845: Sarah Goodyear and Doug Gordon: The War on Cars and Life After Cars
01:26:50||Ep. 845Doug and Sarah's podcastThe War on Cars is a podcast that delivers news and commentary on the latest developments in the worldwide fight to undo a century’s worth of damage wrought by the automobile, approaching the topic from all angles, from politics to pop culture. They release two regular episodes and one Patreon bonus episode per month.Doug and Sarah's BookCars ruin everything. That’s why we need Life After Cars.When the very first cars rolled off production lines, they were a technological marvel, predicted to make life easier and better for everyone; yet a hundred years later, that dream is running on empty.Instead of unbounded freedom, the never-ending proliferation of automobiles has delivered a host of costs, among them the demolition of our neighborhoods, towns, and cities to make way for car infrastructure; an epidemic of violent death; countless hours lost in traffic; isolation from our fellow human beings; and the ongoing destruction of the natural world.That’s why we need Life After Cars. Through historical records, revealing interviews, and unflinching statistics, Sarah Goodyear and Doug Gordon, hosts of the podcast The War on Cars, and former host Aaron Naparstek unpack the scale of damage that cars cause, the forces that have created our current crisis and are invested in perpetuating it, and the way that the fight for better transportation is deeply linked to the fight for a more equitable and just society.Life After Cars expands on the podcast with new interviews and original content—offering something for everyone, from longtime listeners familiar with the harms of car culture to those just beginning to imagine a world with fewer metal boxes zooming around.Cars as we know them today are unsustainable—but there is hope. Life After Cars will arm readers with the tools they need to implement real, transformative change, from simply raising awareness to taking a stand at public forums.It’s past time to radically rethink—and shrink—society’s collective relationship with the automobile.The podcast: The War on CarsThe book: Life After Cars
844. 844: Maya Lilly, part 1: Effective Storytelling and Producing The Years Project
01:35:59||Ep. 844Since I've seen Maya's work on the Years Project with people like executive producers James Cameron and Arnold Schwarzenegger, I was worried I might feel starstruck.Oh wait, she also worked with series creators Joel Bach and David Gelber (of 60 Minutes); chief science advisors podcast guest Joseph Romm and Heidi Cullen; and episode hosts including Cameron, Schwarzenegger, Harrison Ford, Ian Somerhalder, America Ferrera, David Letterman, Gisele Bündchen, Jack Black, Matt Damon, Jessica Alba, Sigourney Weaver.Oh, and the series won an Emmy for Outstanding Documentary or Nonfiction Series.She was engaging, informative, open, and fun. We laughed a bunch We talked about her passion for the art and practice of storytelling. You have to be true to the science, but you can't skimp on the story or take for granted it will work. We also talked about her background that brought her to this level.The Years ProjectIts YouTube pageMaya's curated climate listUPDATE: After we recorded, Maya noted that about halfway in, she said "Bread and Puppet theatre in San Francisco." The actual troop was The San Francisco Mime Troupe.
843. 843: Judith Enck, part 2: The Problem with Plastic (the Book)
28:43||Ep. 843Judith just published The Problem with Plastic: How We Can Save Ourselves and Our Planet Before It’s Too Late.I've read a lot about plastic and hosted many authors. I won't lie. Before starting the book, I thought I should read it because I knew her, but didn't expect much.Instead, I learned a lot new. I found it engaging and compelling. I recommend it.Yes, you'll learn things that are sobering, but you'd rather know than not know, especially things that affect your health and safety and your family's. It also guides you to how to respond, personally, socially, and politically. Judith cares and has experience.Start by listening to our conversation. Then read the book.The Problem with Plastic: How We Can Save Ourselves and Our Planet Before It’s Too LateWEBINAR with co-authors Judith Enck, Adam Mahoney, and Melissa Valliant, January 28, 2026
842. 842: Silvia Bellezza, part 1.5 and 2: When at first you don't succeed
39:44||Ep. 842Since Silvia teaches as a business school, I'll address a leadership aspect of our interaction. I skimped on a leadership step, so we did an episode 1.5, which is my lingo for redoing episode 1 when the person wasn't able to fulfill his or her commitment. That's my responsibility as leader of the interaction.Silvia and I had a wonderful first conversation that led to a commitment that sounded like she'd enjoy it and doable, but in the end wasn't quite. Even if a quick hike north of the city would be enjoyable, catching a Metro-North train from Columbia University isn't that convenient and her schedule may not have bee as flexible as she suspected in our first conversation.For those listening to these conversations to learn the Spodek Method, in our first conversation I didn't check with her how practical the commitment was given her constraints. As the leader of the interaction, I should have asked ahead to imagine her schedule, the logistics of catching the train, and so on. The key measure the first time someone acts on their intrinsic motivation isn't how big it is. It's if they person does it.When someone acts on intrinsic motivation, they'll find it rewarding. If they feel reward, they'll want to do it again and the next time will be bigger, especially if they've always considered acting on sustainability a sacrifice or something that has to be big or any of the other myths people propagate. Sadly, even ardent environmentalists lead people to think of acting more sustainably as something they won't like or won't find rewarding when they use tactics like trying to convince, cajole, coerce, or seek compliance.In this double episode we hear how she did something more practical. At the end, note that she's open to doing more.
841. 841: Sandra Goldmark, part 1: Fixation: How to Have Stuff without Breaking the Planet
41:57||Ep. 841How often does something break that you know could be fixed, but you don't know how and there are no places to fix it? I remember repair stores all over the place, but the field doesn't exist any more. We all know about planned obsolescence and how products are designed to break. Now we feel we have to throw things away and replace them (after avoiding buying things when possible, which is far more than most of us practice).Enter Sandra Goldmark, as a member of a growing movement to fix things and make things fixable. She's also an Ivy League professor at Barnard and the Columbia Climate School, so, no, professors don't have to be out of touch.I met Sandra before the pandemic, at a shop she set up down by the South Street Seaport to repair things. Besides her own book Fixation, she was mentioned in a book (The Repair Revolution) in my sustainability leadership workshop alumni book club.Lest you think people have to be born fixers or educated as engineers, a preconception that I find still holds me back, she shares her background not growing up with those things. On the contrary, she found she enjoyed it and found community.Listen for a basic human approach to fixing things and changing culture.Sandra's home pageHer book, FixationHer page at Barnard
840. 840: Dr. Leonardo Trasande, part 1: Sicker, Fatter, Poorer: The Urgent Threat of Hormone-Disrupting Chemicals to Our Health and Future ... and What We Can Do About It
01:10:11||Ep. 840I found Dr. Trasande quoted in a Washington Post article The health risks from plastics almost nobody knows about: Phthalates, chemicals found in plastics, are linked to an array of problems, especially in pregnancy. He said, "Endocrine-disrupting chemicals are one of the biggest global health threats of our time ... And 2 percent of us know about it---but 99 percent of us are affected by it.”The article said that he said that "at the population level, scientists can see telltale signs that those chemicals are undermining human health, adding to growing male infertility or growing cases of ADHD." This outcome suggests a violation of this nation being founded on protecting life, liberty, and property, and the consent of the governed. I also found from this video, Food Contaminants and Additives, that he reported his results thoroughly, taking care not to venture outside his research.I had to talk to him.We talked about his research, what brought him to a new field, now burgeoning, of learning about chemicals that disrupt our endocrine systems---that is, they mess with our hormones. You'll hear that he didn't intend to go into it. It was (tragically) growing in importance since our hormone systems are becoming increasingly disrupted, as are those of many species.I should be more accurate. They aren't passively being disrupted. Consumers are paying companies to produce chemicals that do it.It sounds slimy and scary. I'd rather it didn't happen, but since it does, I'd rather know than not know. I think you would too.Dr. Trasande's NYU faculty page
839. 839: Saabira Chaudhuri: Consumed: Throwaway Plastic Has Corrupted Us
48:34||Ep. 839Reading Saabira's New York Times piece Throwaway Plastic Has Corrupted Us told me she saw more about plastic and its effect on our culture than most. A quote from it: "The social costs of our addiction to disposable plastics are more subtle but significant. Cooking skills have declined. Sit-down family meals are less common. Fast fashion, enabled by synthetic plastic fibers, is encouraging compulsive consumption and waste."Her tenure at the Wall Street Journal told me she would communicate it effectively, pulling no punches. As much as I prefer not to link to social media, this video review by Chris van Tulleken, bestselling author of Ultra-Processed People, is about as positive a review as I've seen, all the more since he clarifies that he doesn't know her.So I invited her to talk about her book Consumed: How Big Brands Got Us Hooked on Plastic. It launches today (October 7) in the US, so I've only finished the beginning, but it delivers. In our conversation, she describes what to expect when you read it, plus her back story driving her to write it.Many reviews describe her humor. You'll hear that I held back from asking her about how she worked humor into the topic, since she's not a comedian so I wouldn't expect to perform unprepared, but no worry, she made me laugh unprompted and shared more humor from the book. Obviously it's a serious topic, and Saabira's work shows how much more serious than you probably thought, but being depressed doesn't help solve it.Saabira's home pageHer New York Times piece that brought me to her: Throwaway Plastic Has Corrupted UsHer book page for ConsumedThe video review we mention by Chris van Tulleken, bestselling author of Ultra-Processed People